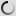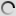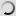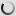Great Grey Owl – Strix nebulosa
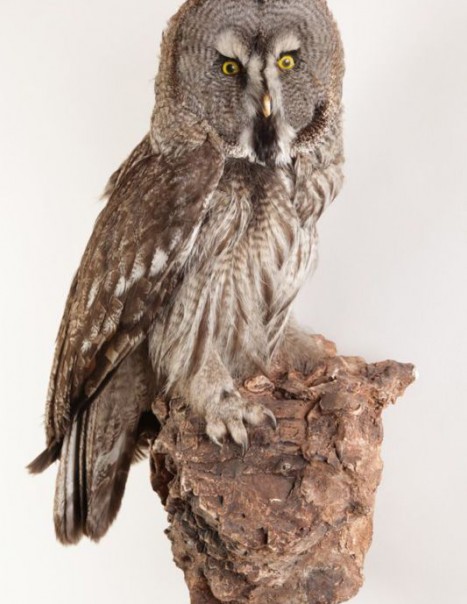
Great Grey Owl – Strix nebulosa
Young have gray and white cryptic plumage.
- S. N. nebulosa
- S.N. lapponica
The male Lapland Owl launches warning cries, Female however emits high-pitched sounds. It attended the boreal forests or dense conifer with open areas like the taiga with wetlands and open fields. It is also present in the pine forests, fir, mountain meadows and in the spruce forests.
Outside the breeding season, this species can be closer to homes.
It is visible from sea level to 1.000 meters above sea level.
It mainly feeds on rodents, birds, amphibians, large insects, voles, mice, squirrels, shrews and rabbits in winter. It can sometimes be diurnal, but primarily hunting at dusk and night, from a perch. It is able to catch prey in the snow only to noise, thanks to its keen sense of hearing. Small rodents are swallowed whole, but the most important prey are broken into pieces. A moment later, it rejects blackish compact balls.
The Great Gray Owl is territorial and very aggressive when it defends the nest. It vigorously attack the intruders and can even give blows to humans who come too close causing serious injury. At the beginning of the breeding season, it performs some displays. The male provides food to the female with the beak and the exchange is made while the two birds have the eyes closed.
The breeding season is between March and July in North America and between March and August in Europe. It is monogamous and the pair formed in January. It often uses abandoned nests of raptors, which on a stump broken tree or an artificial platform on the floor at the foot of a tree.
The female lays 3 to 5 eggs. The importance of the brood depends on food resources. She incubates for about 28 to 36 days while the male feeds the nest.They fledge 25 to 30 days later without knowing fly, but they climb on tilted trees sleep. They are able to fly after one or two weeks. At that time, they are fed by the male. They can reproduce from 1 to 3 years.
The populations are not threatened at this time.