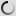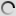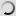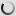Blue Crane – Grus paradisea
Blue Crane – Grus paradisea
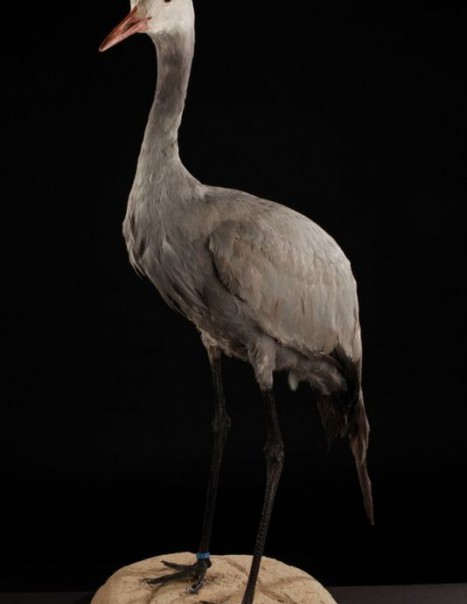
The Blue Crane is the national bird of South Africa.
This species has fully feathered head, without any trace of naked and colored skin.
Head, neck and body are of a uniform bluish gray. On the wings, primaries are black or dark gray. Tertiary are quite long with black ends. They hang almost to the ground and give an elegant look to this crane. The gray breast feathers are also somewhat longer around the base of the neck and the body.
Its beak is relatively short. The eyes are dark brown. Long legs and feet are dark gray to blackish. Both sexes are similar in plumage, but male is larger than the female and the juvenile is pale gray.
It frequents dry plateaus with herbs and sedges, cultivated areas, pastures and fallow fields and wetlands for nesting and sleeping.
It is found mainly in South Africa, a little in Namibia and Etosha
The Blue Crane is more terrestrial than other large cranes. Its short fingers allow it to run better and faster. Shorter beak is also an adaptation to its eating habits because this species feeds mostly in grassy meadows in wetlands.
Breeding season occurs from October to December during the summer. During this season, like other crane species, it makes beautiful courtship.
It nests mainly in grassy areas of the highlands, but also in pastures, cultivated areas, marshes and grasslands near water. The nest is a platform made with aquatic vegetation, often reeds, and also small pebbles. It is always a very simple structure.
It does not migrate, but it performs local and seasonal movements within its distribution and some roam parts of Botswana, Lesotho, Swaziland and Zimbabwe. It has strong flight after running to rise into the air.
The female lays two eggs. Incubation lasts about 30 to 33 days shared between the two parents. Youngs follow the adults early after birth to feed with them.
They are feathered between 3 and 5 months and are sexually mature at the age of 3 or 5 years. It feeds on plant materials such as seeds of herbs and sedges, roots, tubers, cereal residues such as corn and wheat, large insects, grasshoppers, locusts, worms, frogs, crabs, reptiles and small rodents.