Satyr tragopan – Tragopan satyra
Satyr Tragopan – Tragopan satyra
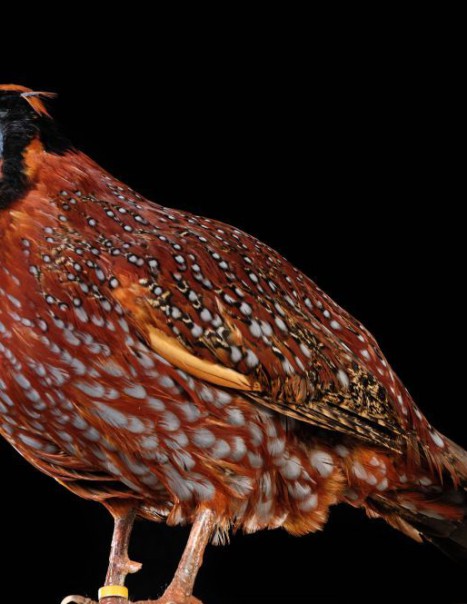
The satyr tragopan is also known as the crimson horned pheasant.
It lives in the hymayan reaches of Bhutan, Nepal, India and Tibet.
In males, the back and wings are brown, covered with small white spots rimmed with black. The head is blue-black and red with a red neck. The beak is short and a small blue horn tip of each side of the head. The underside of the body is red with large round white spots. Continuing the back, tail is brown with a black tip. The legs, strong and rosy, have a spur. Females are brown with ocher stripes and blackish mottling.
It is a mountain bird living in an altitude that can be estimated between 3000 and 4500 meters. During the rainy season, it goes down to 2000 meters. These chickens typically found in cool, damp areas or temperate coniferous forests but also regularly attend the oak forests with a dense understory of bamboo and rhododendron or mixed coniferous and deciduous trees. We can also observe in rocky areas and near small streams for quick flow. In these places the woods are composed of lilac and can be covered with primroses, violets, strawberries as well as myosotys.
It lives in isolated couple. In the wild, it displays a very shy behavior and circumspect. During courtship, the satyr tragopan develops two types of parades and rituals. The breeding season generally occurs from May to June, although some breeders do not breed until July at higher altitudes. The nest, made of sticks and twigs, is installed from the ground in a tree or shrub to a height of up to 6 meters. It is well hidden from view.
In nature, a typical laying consists of two or three eggs while in captivity they can reach six or eight. These eggs, chamois color with reddish brown spots and blotches are incubated for a period of about 28 days. The young are precocial and can survive without food for two days after hatching. The young attend the family and stay with their mother until the age of one year.
They ingest insects, many green vegetation, berries and other fruits, petals, buds and leaves of plants such as laurels, rhododendrons, ferns, daphne and cinnamon trees. They also eat bamboo shoots, seeds of rhododendrons and all kinds of bulbs of the onion family. They particularly appreciate earwigs, ants and roaches. They also consume all kinds of invertebrates such as spiders and centipedes. In captivity they eat fruits and berries.