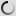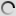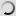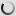Bongo (Young) – Tragelaphus eurycerus
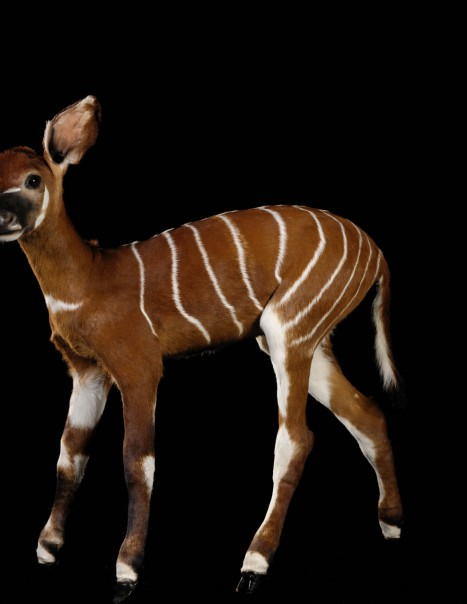
Bongo – Tragelaphus eurycerus
The bongo is an animal that looks like an antilope. Bongo belongs to the order Artiodactyla and family Bovidae herbivorous mammals. They are mainly distributed on the African territory specifically where tropical and humid forests are located. It is particularly in the Congo, Gabon, Uganda, Benin, Cameroon and Sudan among others.
Its coat is brown and red, wearing white vertical stripes on the back and abdomen, it wears high slightly twisted horns that can, in some specimens , measure up to 80 cm. Bongo has along the spine a small dorsal mane from the base of the neck to the base of the tail, also removed the two colors of the animal. Regarding the head it wears some white spots or at least clearer, a bit like a mask. With an average size of 1.25 meters at the shoulder for a length of an average of 2.10 meters, the Bongo can weigh up to over 400kg for a male.
It feeds mainly on grass, moss and leaves its scope.
Females generally have one baby per litter (although cases of twins have been found, there are almost non-existent). Gestation lasts nine months and a half. In general the young is weaned at 4 or 5 months but is completely mature at 2 years. After the withdrawal of its young, the female is again fertilizable for a new range. Bongo can live between 17 and 19 years depending on if they live in captivity or in the wild.
Bongo is not officially endangered, it is even possible to hunt during supervised hunts but his cousin Bongo mountains it is endangered and has only a few hundred representatives on earth.