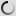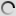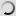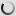Pied Crow – Corvus albus
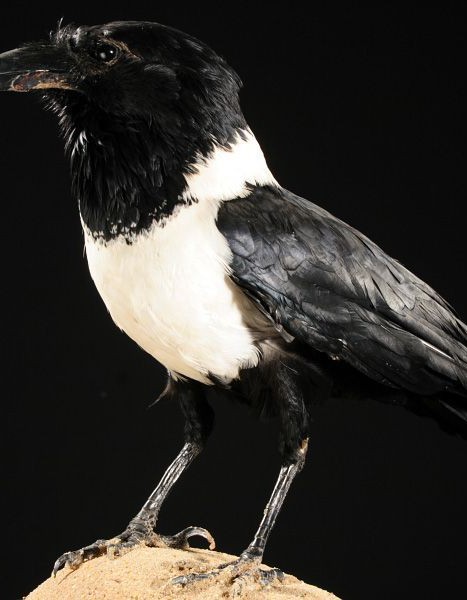
Pied Crow – Corvus albus
This Black and white crow adapts well to different types of habitats, including cities and villages where there are all kinds of foods.
Both adults are similar and have the head, neck and upper chest black with blue and purple hues. The black throat feathers are longer. Its beak is powerful, legs and feet are black. The eyes are dark brown. Juvenile has black parts of the duller plumage and the separation between black and white is less contrast with the gray feather tips.
It frequents open areas and grasslands, discovered countrysides with trees, clearings in forests, savannas, but also the rivers and lakeshores in towns and villages where it finds landfills and slaughterhouses .
It did not attend the thick forests, deserts and mountainous areas. It is found in most of sub-Saharan Africa, Tanzania and Madagascar.The Pied Crow is omnivorous and feed on many insects, mollusks, small vertebrates, amphibians, lizards, rodents, small birds, fish, bats in flight. In the southern parts of the distribution, it also feeds on plants, many seeds, roots and various fruits.
It is known to attack the nests, where it takes the eggs as well as newborns. It feeds in pairs or in small groups, they can gather in large numbers around abundant food sources.
They sleep in dormitories installed in large trees in urban parks. These are then hundreds of birds that are visible.At the beginning of the breeding season, the pie Crow performs courtship displays. In response to these parades, the female adopts a submissive posture. She crouched and vibrates its wings, a typical attitude to invite the male for mating. It has a powerful flight that may be required over long distances with firm beats.
The breeding season varies according to the distribution and rainfall. They are monogamous and pair bonds last all their lives. It nests alone and both adults build the nest, which is a bulky structure made with wood twigs and roots, lined with several kinds of materials such as mud, animal dung, wool, string and herbs. The nest is often placed above and it uses the same site each year, but a new nest is built each time.The female lays 4 to 5 eggs. Both sexes incubate but mainly the female incubates the most.