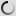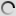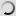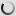Laughing Dove – Spilopelia senegalensis
Laughing Dove – Spilopelia senegalensis
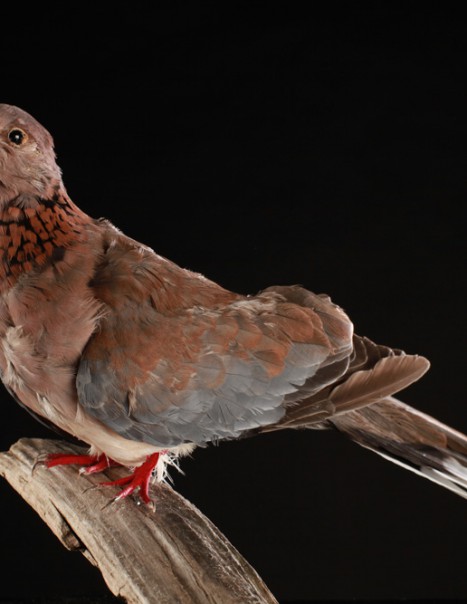
The Laughing Dove is a small long-tailed dove that lives in Sub-Saharan Africa, the Middle East east to the Indian Subcontinent. It appreciates dry scrub and semi-desert habitats where pairs can often be seen feeding on the ground.
A rufous and black chequered necklace gives it a distinctive pattern and is also easily distinguished from other doves by its call.
It has no major nesting site requirements, it will adapt to all kinds of habitats, including the most degraded. Its preferred habitat consists of dry brush, woodlands, thorny bushes, arid but never further away than 10 km from a water point. In Africa, the laughing dove is very common in wooded areas of acacia, in North Africa, it is a bird of the cities, oases and cultivated areas. In India it occupies the woods of deciduous and semi-arid semi deserts. It avoids the tropical rain forests but it colonizes the newly cleared areas.
Nesting season is quite different from regions. In the area of the tropics, it is held at any time of the year, while in others it is considerably smaller. In North Africa, they breed in May and in June in Tunisia and Morocco, while in Egypt they lay their eggs in February. In East Africa, they nest after the rains, in the first part of the dry season. In South Africa and Zimbabwe, they lay during all months of the year, peaking in September.
The nest is a flimsy platform built by the female alone with twigs and dry grasses collected by the male. It is usually placed in a small tree or shrub, where a village building on the outskirts of a city, where the top of the nest of another species. It is reused for several broods. Laying includes two eggs, which are incubated by 2 parents for 12 or 13 days. The young fledge 15 days after hatching.
Their diet consists of grass seed, croton, pollen, oxalis and acacia, leguminous plants and sunflowers, wheat seeds, sorghum and millet. They make great use of cereals and they attend assiduously rubbish dumps; they also love the nectar of flowers, a wide variety of fruits, shoots, termites, insects, mollusks.
Currently the species is not threatened