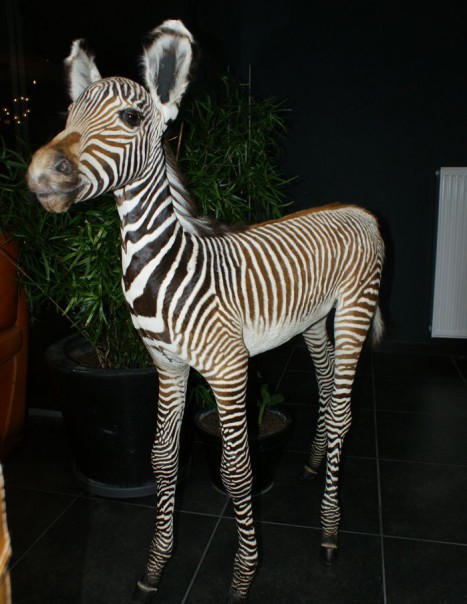
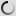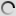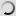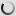Grévy’s zebra – juvenile – Equus grevyi
Grevy’s zebra – Equus grevyi
Also known as the imperial zebra, the Grevy’s zebra is the largest extant wild equid and and the largest and most endangered of the three species of zebra. The other two being the plains zebra and the mountain zebra.
The Grévy’s zebra is found in Kenya and Ethiopia.
Compared with other zebras, it is tall, has large ears and its stripes are narrower.
The Grévy’s zebra lives in semi-arid grasslands where it feeds on grasses, legumes and browse. It can survive up to five days without water. It differs from the other zebra species that it does not live in harems and has few long-lasting social bonds. Male territoriality and mother–foal relationships form the basis of the social system of the Grévy’s zebra.
This zebra is considered to be endangered.
The other subspecies of zebra recognizable are :
- Equus quagga quagga, extinct subspecies
- Equus quagga burchellii, Burchell’s zebra
- Equus quagga boehmi, Grant’s zebra
- Equus quagga borensis, Maneless zebra
- Equus quagga chapmani, Chapman’s zebra
- Equus quagga crawshayi, Crawshay’s zebra