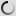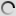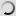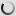Barnacle Goose – Branta leucopsis
Barnacle Goose – Branta leucopsis
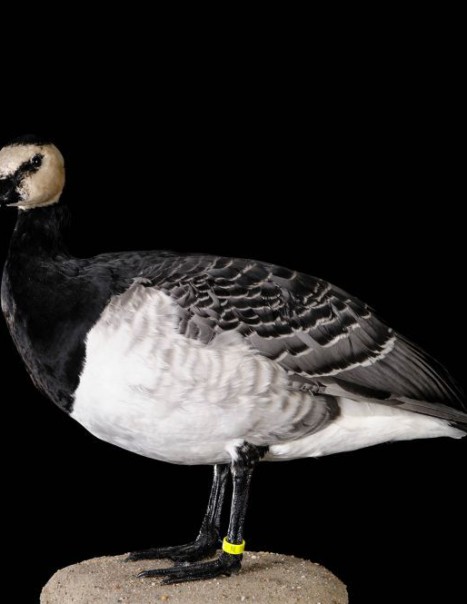
The barnacle goose is a small goose. It is immediately identifiable by its black neck and chest, very small white head, gray striped top with contrasting pale below. We can find a few similarities with canadian goose but it has a longer neck, pale or brown chest, in any case, black. Barnacle goose has a black triangular beak, black legs and a white rump.
In the summer, it attends the cliffs and scree arctic islands. In winter, it lives in the flooded meadows and coastal marshes, low banks of marine bays and mudflats at low tide.
They live in Greenland, Spitsbergen and New Zealand. They begin their migration in late August or early September. Never mixed, they reach the shores of Scotland, Ireland, the west coast of Britain and the coast of Germany and the Netherlands. There are a few dozen individuals in the Bay of Somme or the Mont St Michel. However, in very severe winters, France hosted until 8000 barnacle geese.
Its range is now broader and affects all the small bays and sheltered estuaries.
Nesting season begins soon after the return in the Arctic. Every bird chooses its partner for the season and these links can sometimes persist throughout life. Barnacle geese gather to nest in colonies. The nest is built mainly of plants and lined with down, it is built on the ledge of a cliff, on a non-remote island of the coast or even open tundra. The site is sometimes shared with guillemots. The female lays 3-5 eggs, which it incubates alone for a period ranging from 24 to 25 days while the male mounts a vigilant guard nearby. Young are active at hatching and can fly after 40 or 45 days. The family group remains together during migration and wintering.
As geese are mainly vegetarian, the grass dominates the regime. They eat also shoots of various marine plants. In winter, when the grass is less dense, it eats algae, aquatic insects, molluscs and crustaceans. The species feeds at any time of day and prefers the grass of the coastal zone periodically submerged by floods. If it does not have, it falls back on the meadows located behind the coast.
Its life is estimated at 19 years.